Bulk SMS in Australia: A Complete Guide

What is Bulk SMS?
Bulk SMS, short for Bulk Short Message Service, is a powerful communication tool that allows businesses to send a high volume of text messages to multiple recipients at once. Unlike personal SMS, which is typically used for one-on-one communication, bulk SMS is designed to reach hundreds or even thousands of people simultaneously, making it an ideal choice for businesses looking to communicate efficiently with a large audience.
How Bulk SMS Works
Bulk SMS messages are sent through specialized platforms or SMS gateways that connect directly to mobile networks. When a business sends out a bulk SMS campaign, their message is routed through the SMS gateway and then distributed to mobile carriers. These carriers deliver the messages to each recipient’s phone, ensuring they arrive quickly and reliably.
This seamless process involves just a few steps on the business side. Using an SMS platform, businesses can upload or select a contact list, type out a message, and schedule or send it immediately. The bulk SMS provider takes care of the technical routing and delivery, enabling businesses to focus on their message content and campaign goals.
Types of Bulk SMS Messages
Bulk SMS can be classified into two main categories: promotional and transactional messages.
- Promotional Messages: These messages are designed to engage customers, promote products or services, and drive sales. Examples include special offers, discounts, event invitations, and reminders of limited-time deals. Promotional messages help brands stay top-of-mind and encourage customers to take action.
- Transactional Messages: Transactional SMS messages are used for notifications and updates that are relevant to specific customer actions or events. Examples include order confirmations, appointment reminders, account notifications, and one-time passwords (OTPs). These messages are often time-sensitive and help build trust by providing valuable, relevant information.
Use Cases for Bulk SMS
Bulk SMS is an incredibly versatile tool used across many industries. Here are some of the most common ways businesses are using bulk SMS today:
- Retail: Promote sales, send discount codes, and inform customers about new product launches.
- Healthcare: Send appointment reminders, health tips, and important updates.
- Finance: Deliver transaction alerts, payment reminders, and account notifications.
- Education: Notify students or parents about events, cancellations, or application deadlines.
- Hospitality: Confirm reservations, share booking details, and send follow-up surveys for feedback.
- Real Estate: Keep potential buyers updated on new listings, open houses, and market trends.
Why Bulk SMS is So Effective
Bulk SMS stands out from other marketing methods due to its immediacy, high open rates, and the personal nature of SMS communication. Studies show that SMS messages boast an open rate of over 90%, with most recipients viewing the message within minutes of receiving it. This level of engagement is unmatched by other communication channels, making bulk SMS a valuable asset for businesses that need their messages to be seen quickly.
In Australia, where mobile phone penetration is high, bulk SMS offers businesses a direct line to their audience, helping them stay connected, drive engagement, and strengthen customer relationships. Whether it’s a promotion, an urgent update, or a friendly reminder, bulk SMS ensures that businesses can reach their customers instantly, wherever they are.

The History of Bulk SMS

Understanding the history of bulk SMS provides insight into how this technology evolved into the powerful business tool it is today. From its humble beginnings as a simple text-based communication method to a sophisticated marketing channel, SMS has transformed significantly over the past few decades.
The Early Days of SMS (1980s - 1990s)
SMS, or Short Message Service, was first developed in the 1980s as part of the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) standard. The idea was to create a quick, text-based form of communication that could be sent over mobile networks. In 1992, engineer Neil Papworth sent the first-ever SMS, simply saying “Merry Christmas.” This initial message laid the foundation for SMS as a new way to communicate, though it was initially limited to short, personal exchanges.
In these early days, SMS messages had a character limit of 160 due to technical constraints within the GSM standard. Despite this limitation, the new form of messaging quickly gained popularity as mobile phone adoption increased. By the late 1990s, mobile carriers began offering SMS packages, making it a more accessible and affordable option for personal communication.
SMS Becomes Mainstream (1990s - Early 2000s)
As SMS grew in popularity, businesses started to recognize its potential for direct, immediate communication. Companies began experimenting with SMS for customer notifications, though it was still primarily used for person-to-person communication. Internationally, SMS usage surged as it became a universal standard across carriers, allowing people to send text messages to anyone, regardless of their network or location.
During this time, SMS messaging for businesses was limited in scope and often expensive, requiring dedicated infrastructure for bulk messaging. This meant only large corporations or tech-savvy organizations experimented with SMS for reaching their customers, and most business use cases were limited to essential notifications or reminders.
The Birth of Bulk SMS (Early to Mid-2000s)
The early 2000s marked the emergence of SMS gateways, which made bulk messaging more accessible to businesses. These gateways allowed companies to send mass messages via software rather than physical mobile devices, significantly reducing costs and infrastructure requirements. As a result, small to medium-sized businesses began to see the potential of SMS as a scalable communication tool.
Marketers began to recognize the unique advantages of SMS over other channels, especially the fact that SMS messages had far higher open rates than email. However, as SMS marketing began to grow, so did the need for regulatory oversight. In Australia, the Spam Act 2003 was introduced to set strict guidelines on SMS marketing, ensuring businesses obtained consent before sending messages and provided opt-out mechanisms.
The SMS Boom (Mid-2000s - 2010s)
During the mid-2000s to early 2010s, SMS became a staple for businesses across a range of industries. Technological advancements made it easier for companies to integrate SMS into their existing systems, allowing for more sophisticated applications. CRM systems and other marketing tools began incorporating SMS features, enabling businesses to personalize messages, automate campaigns, and track results.
The emergence of SMS aggregators also played a key role in popularizing bulk SMS. Aggregators connected with multiple telecom carriers to provide businesses with reliable and cost-effective messaging services, simplifying the process of sending messages on a large scale. This period saw a shift from SMS as a simple communication tool to a central part of many companies' customer engagement strategies.
Challenges and Innovations (2010s - Present)
As digital marketing evolved, SMS began facing competition from new messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and email. Despite this, SMS remained valuable due to its immediacy, simplicity, and universal accessibility. To keep up with the competition, SMS technology also started evolving.
Rich Communication Services (RCS) emerged as an enhancement to traditional SMS, allowing for interactive features such as images, buttons, and links, especially on smartphones. Although RCS is not yet as widely adopted as SMS, it represents the next generation of messaging with the potential to make SMS more engaging.
Another significant development has been the integration of artificial intelligence and automation into bulk SMS, enabling businesses to create intelligent workflows, predictive messaging, and even two-way SMS chat experiences. These advancements have helped SMS remain relevant as part of a modern, omnichannel marketing strategy.
The Current State and Future of Bulk SMS
Today, bulk SMS is a vital tool for businesses seeking instant, high-engagement communication. The high open rates and fast delivery make it ideal for industries like retail, finance, healthcare, and hospitality, where timely messages are critical. As 5G technology expands, SMS is expected to become even faster, possibly enabling richer messaging capabilities and a smoother customer experience.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also shaping the future of bulk SMS. With AI, businesses can use predictive analytics to send messages at the optimal time or tailor content based on user behaviour. SMS remains an essential part of the digital marketing mix, especially in markets like Australia, where mobile penetration is high and consumers are accustomed to SMS notifications.
As we look to the future, bulk SMS will likely continue evolving with new technologies like RCS and 5G. With these developments, SMS will remain a cornerstone of effective business communication, valued for its reach, reliability, and unmatched engagement.
The Importance of Bulk SMS in Australia
For Australian businesses, bulk SMS is an incredibly effective communication tool that bridges the gap between brands and consumers. SMS has one of the highest engagement rates of any marketing channel, and in a country with high mobile phone penetration, it offers a direct, reliable way to reach customers. Here’s why bulk SMS is particularly valuable in the Australian market:
1. High Mobile Penetration and Engagement in Australia
Australia is a mobile-first country, with over 90% of Australians owning a mobile phone. This high penetration means that SMS provides unparalleled reach, with almost every adult being accessible via text message. Furthermore, SMS open rates exceed 90%, and most recipients read their messages within minutes, a level of immediacy that email and other channels struggle to match.
Australian consumers are accustomed to receiving SMS updates, reminders, and alerts from businesses, making bulk SMS an ideal way to stay top-of-mind and reach customers wherever they are.
2. Reaching Customers Directly and Instantly
Bulk SMS allows businesses to deliver messages directly to customers’ mobile phones, bypassing potential distractions or inbox clutter. Unlike email, where messages can go unread or end up in spam folders, SMS is delivered straight to the recipient, ensuring visibility. This immediacy is crucial for time-sensitive communications, such as appointment reminders, limited-time offers, and urgent updates.
For example, during peak retail periods like Boxing Day sales or end-of-year clearance events, retailers can use bulk SMS to reach customers instantly, boosting traffic and encouraging timely action.
3. Cost-Effective and High ROI Marketing Channel
Compared to other advertising methods, bulk SMS is highly cost-effective. It enables businesses to reach large audiences at a fraction of the cost of print, radio, or television ads. Since SMS has high open and engagement rates, the return on investment (ROI) is significantly higher. For small and medium-sized businesses in Australia, where budgets may be limited, SMS marketing is an affordable yet impactful way to reach customers and drive conversions.
Additionally, many bulk SMS providers offer flexible pricing options, allowing businesses to purchase SMS credits based on volume or set monthly plans, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes.
4. Meeting Customer Expectations for Fast and Reliable Communication
Australian consumers expect fast and reliable communication from the brands they engage with, particularly when it comes to transactional information like delivery updates, order confirmations, or payment reminders. Bulk SMS allows businesses to meet these expectations, providing a fast, direct communication line that reassures customers and enhances trust.
SMS is also less intrusive than other forms of communication, as it doesn’t require the recipient to be actively using an app or social media platform to receive messages. This makes SMS a convenient option for communicating with customers on their terms.
5. Supporting Compliance and Customer Privacy
Australia has strict regulations when it comes to digital marketing and customer privacy. The Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) enforces the Spam Act 2003, which sets rules around sending commercial SMS messages. Bulk SMS providers in Australia offer tools and features that help businesses stay compliant, such as automatic opt-out mechanisms and data protection measures.
This compliance is essential for maintaining customer trust. When businesses respect customers’ privacy preferences and follow legal guidelines, they foster better relationships and demonstrate a commitment to responsible marketing.
6. Flexibility Across Different Industries
Bulk SMS is incredibly versatile, allowing businesses across a wide range of industries to tailor SMS marketing to their needs. Here’s how some Australian sectors are effectively using bulk SMS:
- Retail: Retailers send SMS alerts about sales, new arrivals, and promotions, driving foot traffic and online sales.
- Healthcare: Clinics and medical providers use SMS reminders for appointments, reducing no-shows and improving patient care.
- Hospitality: Restaurants and hotels confirm reservations, share booking details, and gather customer feedback via SMS.
- Education: Schools and universities notify students and parents of events, closures, and critical updates.
- Finance: Banks and financial institutions use SMS to alert customers to transactions, account changes, and security notices.
No matter the industry, bulk SMS provides a simple, adaptable solution for businesses that want to connect with their customers in real-time.
7. Ideal for Time-Sensitive Communications
One of the standout features of SMS is its ability to reach recipients almost instantly. This is crucial for businesses that rely on time-sensitive messaging. In scenarios where immediate action is needed—such as last-minute sales, flash discounts, or urgent notifications—SMS is the most reliable way to ensure that customers see and respond to the message quickly.
For example, during events like Black Friday or a one-day-only sale, an SMS campaign can notify customers instantly, creating a sense of urgency that drives prompt action. The quick delivery of SMS also makes it ideal for industries like healthcare and finance, where timely notifications are essential for customer satisfaction and safety.
8. Integrating SMS with Digital Marketing Campaigns
SMS complements other marketing channels like email and social media, allowing businesses to create unified, omnichannel campaigns. By integrating SMS with these channels, businesses can engage customers at multiple touchpoints, reinforcing messages and boosting engagement. For instance, an email campaign might provide detailed information about a new product, while a follow-up SMS can remind customers of a limited-time discount on that product.
This cohesive approach enhances brand presence and enables businesses to reach customers through their preferred channels, creating a seamless experience that leads to higher engagement and loyalty.
Benefits of Bulk SMS for Businesses

Bulk SMS offers several unique advantages that make it a valuable marketing and communication tool for businesses. From cost savings to high engagement rates, bulk SMS provides benefits that few other channels can match. Here’s a closer look at the key advantages:
1. Immediate Reach and High Open Rates
One of the primary benefits of bulk SMS is its immediacy. Text messages are typically delivered within seconds, and most recipients read them almost instantly. Research shows that SMS has an open rate of over 90%, far exceeding email or social media. This makes SMS an ideal channel for time-sensitive messages, ensuring your content is seen quickly.
For example, businesses can use SMS to notify customers of flash sales, booking confirmations, or urgent updates. This immediate reach is particularly valuable for industries like healthcare, retail, and finance, where timely communication can directly impact customer satisfaction.
2. Cost-Effective Marketing with High ROI
Compared to traditional advertising channels such as TV, print, or even digital ads, bulk SMS is highly cost-effective. Sending an SMS message costs only a few cents, making it accessible even to small businesses with limited budgets. With the high open and engagement rates that SMS provides, businesses can achieve a strong return on investment (ROI) with minimal expense.
Bulk SMS is especially advantageous for startups and small businesses that want to reach a broad audience without incurring the high costs associated with other marketing channels. By focusing on a targeted, direct approach, businesses can save money while achieving meaningful results.
3. High Engagement and Response Rates
In addition to high open rates, SMS messages also boast impressive engagement and response rates. Studies show that SMS messages have a response rate of around 45%, significantly higher than email or social media. This high level of engagement makes SMS particularly effective for driving immediate action, whether it’s completing a purchase, filling out a survey, or confirming an appointment.
The personal and direct nature of SMS also encourages recipients to interact with the message. Unlike emails that may go unopened or social media posts that can be lost in the feed, SMS commands attention and elicits quick responses, helping businesses reach their engagement goals.
4. Versatility Across Various Use Cases
Bulk SMS can be adapted to a wide range of use cases, making it a versatile tool for businesses across different industries. Here are a few common examples:
- Promotions and Offers: Retailers can send SMS campaigns featuring exclusive discounts, seasonal sales, or limited-time offers, encouraging customers to make purchases.
- Appointment Reminders: Healthcare providers use SMS to remind patients of upcoming appointments, reducing no-shows and improving operational efficiency.
- Order Updates: E-commerce businesses can notify customers of order status updates, shipment tracking, and delivery confirmations.
- Feedback and Surveys: Companies can use SMS to gather customer feedback or conduct surveys, providing valuable insights into customer satisfaction and preferences.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Financial institutions often use SMS for 2FA to secure online accounts, ensuring an additional layer of security for their customers.
This versatility allows businesses to integrate SMS into various stages of the customer journey, from acquisition and engagement to retention and support.
5. Measurable and Data-Driven Results
Bulk SMS platforms typically come with analytics and reporting features, allowing businesses to measure the performance of their campaigns. Key metrics include delivery rates, open rates, click-through rates (for SMS with links), and response rates. By tracking these metrics, businesses can gain insights into what’s working and what needs improvement.
This data-driven approach helps companies make informed decisions, optimize their messaging strategies, and refine future campaigns. Analytics also provide a clear picture of the ROI, making it easier for businesses to justify their SMS marketing spend and adjust budgets accordingly.
6. Personalization and Customer Engagement
Bulk SMS platforms allow businesses to personalize messages by using customer data such as names, order details, or previous interactions. Personalized messages tend to resonate better with recipients, leading to higher engagement and response rates. For example, a retail brand can send a message saying, “Hi Sarah, we’ve got a special discount just for you!” to create a more personal connection.
This level of personalization not only enhances the customer experience but also strengthens the brand-customer relationship. When customers feel valued, they’re more likely to engage with the brand, leading to improved loyalty and retention.
7. Environmentally Friendly and Sustainable
Bulk SMS is a digital form of communication, which means it doesn’t rely on physical resources like paper or ink. This makes it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional marketing methods such as direct mail. For businesses that prioritize sustainability and corporate social responsibility, SMS provides a way to engage customers while minimizing environmental impact.
As awareness around sustainability grows, consumers are increasingly drawn to businesses that demonstrate eco-conscious practices. Using SMS as part of a sustainable marketing strategy can enhance brand perception and appeal to environmentally-minded customers.
8. Easily Integrates with Other Marketing Channels
Bulk SMS is highly compatible with other digital marketing channels, allowing businesses to create a cohesive, omnichannel strategy. For instance, an e-commerce store might send an email with product details, followed by an SMS reminder for a limited-time discount, or a retail brand might use SMS to remind customers about an upcoming event promoted on social media.
By combining SMS with other channels, businesses can engage customers at multiple touchpoints, reinforcing their message and increasing the likelihood of conversion. This integrated approach ensures that customers receive consistent communication across all platforms, improving brand recognition and trust.
9. Regulatory Compliance and Customer Trust
Bulk SMS providers in Australia typically include features that help businesses comply with local regulations, such as the Spam Act 2003. This ensures that businesses can legally and ethically engage customers via SMS, providing them with options to opt out if they choose.
Compliance with SMS regulations not only protects businesses from potential penalties but also builds customer trust. When customers know they can easily unsubscribe or manage their preferences, they’re more likely to view the brand as respectful and trustworthy, which enhances loyalty and brand reputation.
Industries Leveraging Bulk SMS in Australia
Bulk SMS is a versatile tool that serves a wide range of industries across Australia. Its effectiveness lies in its flexibility and immediacy, making it adaptable for everything from promotions to critical notifications. Here’s a look at how different Australian industries are leveraging bulk SMS to achieve their unique goals:
Retail
Retailers in Australia use bulk SMS to stay connected with their customers and drive sales. With high open and response rates, SMS is perfect for time-sensitive promotions, flash sales, and special offers. During major shopping events like Boxing Day and end-of-season sales, retailers can reach their audience directly, ensuring maximum visibility and engagement. Bulk SMS also allows retailers to send targeted messages, such as “VIP” discounts for loyal customers, which enhances brand loyalty.
Example Use Case: “20% OFF this weekend only! Show this message in-store or use code SMS20 online. Offer ends Sunday.”
Healthcare
The healthcare industry relies on bulk SMS to improve patient engagement and reduce no-show rates. Medical practices, clinics, and hospitals use SMS to send appointment reminders, health updates, and test results. By automating these reminders, healthcare providers can ensure patients are well-informed while reducing administrative workload.
Example Use Case: “Reminder: Your dental appointment with Dr. Lee is scheduled for Tuesday, 10:00 AM. Reply YES to confirm or call 1234 5678 to reschedule.”
Hospitality
Restaurants, hotels, and event venues use bulk SMS to enhance the guest experience and streamline reservations. SMS allows businesses to confirm bookings, send reminders, and even request feedback after a visit. In a time-sensitive industry like hospitality, SMS provides an efficient way to communicate with customers, reducing missed bookings and improving overall service quality.
Example Use Case: “Your table at The Olive Grove is reserved for 7:00 PM tonight. Please reply CONFIRM or CANCEL. We look forward to seeing you!”
Education
Schools, universities, and training institutions use bulk SMS to communicate important updates with students, parents, and staff. SMS is especially valuable for notifying students of timetable changes, event reminders, or weather-related closures. By using SMS, educational institutions can ensure timely communication, particularly when urgent updates are required.
Example Use Case: “Reminder: Parent-Teacher conferences will be held on March 15 from 4-7 PM. Please confirm your attendance by replying YES.”
Finance
Financial institutions, including banks and insurance providers, use SMS for secure, reliable communication with their clients. From transaction alerts to payment reminders, bulk SMS helps these organizations keep customers informed while enhancing account security. With two-factor authentication (2FA) becoming a standard, SMS also plays a vital role in protecting users’ sensitive information.
Example Use Case: “Alert: Your account was accessed from a new device. If this was not you, please contact customer support at 1234 5678.”
Real Estate
Real estate agents and property managers use SMS to engage potential buyers and tenants, sending alerts about new listings, open houses, and price changes. Bulk SMS allows agents to reach interested clients immediately, increasing the likelihood of successful property viewings and sales. Additionally, property managers can use SMS to inform tenants of maintenance updates or rent payment reminders.
Example Use Case: “Open House Alert: 3-bedroom home at 12 Sunny Ave is open this Saturday from 1-3 PM. Don’t miss it!”
Logistics and E-commerce
E-commerce and logistics companies leverage bulk SMS to keep customers updated on their orders. SMS notifications for shipping updates, delivery confirmations, and estimated arrival times help businesses manage customer expectations and build trust. For time-sensitive deliveries, SMS offers the reassurance that customers will receive updates right when they need them.
Example Use Case: “Your package from Store XYZ is out for delivery and will arrive today by 5 PM. Track your package here: [link].”
Non-Profit Organisations
Non-profits and charitable organisations use bulk SMS to mobilize support, update volunteers, and engage with donors. SMS is an effective way to reach supporters directly, whether to announce upcoming events, request donations, or provide updates on specific campaigns. This direct communication channel enables non-profits to build a stronger, more active community.
Example Use Case: “Join us this Saturday at 10 AM for our community clean-up event. Reply YES to volunteer or visit [link] for more details.”
Government and Public Services
Government agencies and public service providers use SMS to communicate critical information with citizens, especially during emergencies. From weather alerts to important public health updates, bulk SMS enables immediate, wide-reaching communication that ensures everyone stays informed and safe.
Example Use Case: “Emergency Alert: Severe weather expected in your area. Stay indoors and follow safety instructions. Visit [link] for updates.”
Each industry has unique communication needs, but they all benefit from bulk SMS’s ability to deliver time-sensitive information quickly and reliably. By tailoring SMS campaigns to meet these specific requirements, businesses and organizations across Australia can improve customer engagement, boost satisfaction, and build stronger connections with their audience.
This diverse range of applications demonstrates the versatility of bulk SMS and its potential to enhance communication across sectors. Whether for promotions, reminders, security alerts, or public safety updates, bulk SMS provides Australian industries with a direct line to their audience, making it an invaluable tool for reaching people when it matters most.
Comparing Bulk SMS with Other Marketing Channels
While bulk SMS has proven itself as a highly effective communication tool, it’s worth understanding how it compares to other popular marketing channels. Each channel has its own strengths, and knowing where SMS excels can help businesses create more cohesive and effective marketing strategies. Here’s a comparison of bulk SMS with email marketing, social media, direct mail, and push notifications:
1. Bulk SMS vs. Email Marketing
Open Rates and Engagement: SMS has significantly higher open rates than email. Studies show that over 90% of SMS messages are read within minutes of being received, whereas email open rates hover around 20-30%. For businesses needing immediate engagement, SMS is the clear winner.
Content Length and Personalization: Email allows for longer, more detailed content, which is beneficial for newsletters, blog updates, and product information. SMS, on the other hand, is best for concise messages with a clear call-to-action. While both channels can be personalized, SMS has a more personal feel due to its direct nature.
Best Use Cases: SMS works well for urgent updates, limited-time offers, reminders, and alerts, where immediacy is essential. Email is better suited for longer-form content, promotional offers with detailed descriptions, and monthly newsletters.
Compliance and Deliverability: Both SMS and email are regulated channels, but SMS often reaches customers more reliably. Emails can end up in spam folders, while SMS messages are delivered directly to recipients’ mobile devices. In Australia, SMS must comply with the Spam Act 2003, while email marketing adheres to the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) guidelines.
2. Bulk SMS vs. Social Media
Reach and Visibility: SMS messages go directly to the recipient’s phone, making them hard to ignore. Social media posts, however, compete with a high volume of content and can easily get lost in users’ feeds. SMS is ideal for direct communication, while social media is better for broader brand awareness and community engagement.
Engagement Levels: SMS has a higher engagement rate due to its personal and direct nature. In contrast, social media engagement varies greatly depending on platform algorithms, post timing, and content quality. SMS provides a reliable way to reach customers, whereas social media’s reach can be inconsistent.
Content Flexibility: Social media allows for rich content—images, videos, and stories—whereas SMS is limited to text (or multimedia in the case of MMS). For visual branding or storytelling, social media is the preferred choice, while SMS is effective for delivering quick, actionable messages.
Best Use Cases: SMS is ideal for direct communication, such as alerts, reminders, and promotions. Social media is more suited for building brand identity, engaging with followers, and sharing visual content.
3. Bulk SMS vs. Direct Mail
Cost and Speed: Direct mail campaigns are costly and can take days to reach recipients, making them impractical for time-sensitive promotions. SMS, by contrast, is affordable and instantaneous, with messages reaching recipients within seconds.
Personalization and Targeting: While direct mail can be personalized to some extent, SMS allows for more precise targeting and personalized content, like using recipients’ names, purchase history, or preferences.
Response Rate and Tracking: SMS campaigns have higher response rates than direct mail and are easier to track. SMS platforms offer analytics on delivery, open, and click-through rates, whereas direct mail requires additional tracking methods, such as QR codes or custom URLs.
Best Use Cases: Direct mail works best for high-value promotions or when businesses want to send tangible items like brochures or samples. SMS is a better choice for immediate, high-engagement campaigns where cost and speed are critical.
4. Bulk SMS vs. Push Notifications
Accessibility and Opt-In: Push notifications require users to have a specific app installed and to opt-in to notifications. SMS, on the other hand, only requires the recipient’s mobile number and permission, making it more accessible for reaching a broad audience.
Open and Response Rates: SMS messages have high open and response rates, while push notification engagement can vary significantly based on the type of app, content, and timing. Push notifications are often ignored or disabled by users, whereas SMS notifications are typically read immediately.
Best Use Cases: Push notifications are ideal for app-based updates, like reminding users to check a feature or sending updates for active app users. SMS is effective for reaching both app and non-app users, making it versatile for any business looking to engage customers directly.
5. Bulk SMS as Part of an Omnichannel Strategy
While each channel has its strengths, SMS works exceptionally well when integrated into an omnichannel strategy, complementing other channels like email, social media, and push notifications. For example, a business could send a detailed promotional email with product information and then follow up with an SMS reminder about the promotion’s expiration. Similarly, an SMS can be used to re-engage customers who haven’t responded to a social media promotion or email.
Examples of Omnichannel SMS Use Cases:
- Abandoned Cart Reminders: A retail brand could send an email to remind customers of items left in their cart, followed by an SMS with a discount code to encourage purchase completion.
- Event Promotion: A business promoting an event might announce it on social media, send a follow-up email with event details, and then use SMS as a reminder on the day of the event.
- Customer Support: For support inquiries, a business could use SMS to confirm the receipt of a support ticket, follow up with email for detailed instructions, and send a satisfaction survey through SMS afterward.
Integrating SMS with other marketing channels creates a seamless experience for customers, allowing businesses to reach people through their preferred channels while reinforcing key messages. This approach not only improves engagement but also strengthens brand consistency, as customers receive aligned messaging across platforms.
Technical Aspects of Bulk SMS
For businesses looking to maximize the impact of bulk SMS, understanding the technical details can help optimize performance and ensure reliability. From message encoding and character limits to delivery protocols and sender IDs, here’s a look at the essential technical aspects of bulk SMS.
1. SMS Gateways and Aggregators
An SMS gateway is the system that enables the transmission of SMS messages from a business to mobile carriers, which then deliver the messages to recipients. SMS aggregators connect with multiple carriers to ensure broad delivery capabilities and route messages effectively. By working with aggregators, bulk SMS providers can offer businesses reliable and scalable solutions for reaching customers across different networks.
2. Message Encoding and Character Limits
SMS supports several encoding formats, each affecting the message’s character limit. The two main encoding types are GSM-7 and UCS-2:
- GSM-7: The default encoding format for SMS, GSM-7 supports Latin characters and allows for 160 characters per message. It’s the most common encoding for English and other Western languages, making it ideal for businesses targeting general audiences.
- UCS-2: This encoding format supports non-Latin characters, such as those in Chinese, Arabic, or emojis. However, UCS-2 messages are limited to 70 characters per SMS due to the larger data requirements. When businesses need to reach audiences using non-Latin scripts or want to include special characters, UCS-2 is necessary, though it reduces the character limit.
For messages exceeding these character limits, SMS gateways use concatenation to split the message into multiple segments, which are then reassembled by the recipient’s phone. This process ensures longer messages are delivered in full, although it may increase costs as each segment counts as an individual SMS.
3. Delivery Reports and Status Codes
Delivery reports, or DLRs, provide information on whether an SMS has been successfully delivered to the recipient. These reports include status codes that indicate various delivery outcomes, such as:
- ✅ Delivered: The message was successfully delivered to the recipient’s phone.
- ⌛ Buffered: The message is in a queue and will be delivered when the recipient’s phone is available.
- ❌ Failed: The message couldn’t be delivered, often due to issues like an invalid phone number or network error.
These reports allow businesses to monitor campaign effectiveness, track message delivery rates, and identify any issues affecting performance. DLRs are particularly useful for tracking critical notifications where confirmation of delivery is essential.
4. Latency and Message Delivery Speed
Message latency refers to the time it takes for an SMS to travel from the sender to the recipient. Several factors can impact latency, including network congestion, message volume, and carrier priorities. For businesses, low latency is crucial for time-sensitive communications like two-factor authentication (2FA), limited-time offers, and urgent alerts.
Bulk SMS providers use optimized routing and priority queuing to reduce latency, ensuring that messages are delivered promptly. Some providers also offer premium routing options, which prioritize delivery by sending messages through the fastest available channels, further minimizing delays.
5. Sender IDs and Alphanumeric Codes
Sender IDs are the names or numbers displayed as the message sender on recipients’ phones. There are several types of sender IDs:
- Numeric Sender ID: A standard phone number that allows for two-way communication, enabling recipients to reply directly to the message.
- Alphanumeric Sender ID: A custom identifier, typically the brand name (e.g., “MobileMsg”), that makes the message appear more professional. Alphanumeric sender IDs do not support replies but are effective for branding and recognition.
- Short Codes: Shortened numeric codes (usually 5-6 digits) used for high-volume messaging or campaigns. Short codes can support two-way communication and are easy for customers to remember.
In Australia, there are regulations around the use of alphanumeric sender IDs and short codes, particularly for marketing messages. Bulk SMS providers often handle these regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance with Australian laws while giving businesses flexibility in choosing the most suitable sender ID.
6. Throttling and Rate Limits
Throttling is the process of controlling the rate at which messages are sent to prevent network overload and avoid potential carrier restrictions. Bulk SMS providers implement rate limits, which specify the maximum number of messages that can be sent per second or minute.
For large campaigns, throttling helps ensure that messages are delivered without compromising speed or reliability. Businesses can work with their SMS provider to set optimal throttling rates based on campaign goals and message volume, ensuring smooth delivery even during high-traffic periods.
7. SMS APIs and Integration Capabilities
Many businesses integrate bulk SMS with their existing systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, e-commerce websites, or marketing automation tools, using SMS APIs. An SMS API is a programming interface that allows businesses to send SMS messages programmatically, enabling seamless automation and customization.
Common API methods include:
- Sending SMS: Triggering SMS sends for single messages or bulk campaigns.
- Scheduling SMS: Setting future send times for automated campaigns.
- Fetching Delivery Reports: Accessing real-time delivery data for monitoring performance.
- Two-Way SMS Support: Managing incoming replies for customer interactions.
SMS APIs offer extensive integration capabilities, enabling businesses to set up workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and ensure consistent communication with customers across channels.
8. Security and Data Protection
For businesses handling sensitive customer information, security is a top priority in SMS communication. Bulk SMS providers employ encryption, secure data storage, and authentication protocols to safeguard data. API keys, IP whitelisting, and two-factor authentication are commonly used to protect access to SMS platforms and prevent unauthorized messaging.
Data protection is particularly important in Australia, where the Privacy Act 1988 outlines strict requirements for handling personal information. Reputable SMS providers offer compliance tools and data management features that help businesses meet these legal obligations and protect customer privacy.
9. Fallback Mechanisms and Retry Logic
Sometimes, SMS messages may fail to deliver on the first attempt due to network issues, device availability, or other factors. Bulk SMS platforms employ fallback mechanisms, or retry logic, to automatically reattempt delivery if a message fails. This ensures that businesses can still reach customers, even if there are temporary delivery issues.
For time-sensitive messages, such as 2FA codes, these fallback mechanisms are essential for maintaining service reliability. Businesses can often configure retry settings, such as the number of attempts or delay between retries, to optimize delivery based on campaign needs.
Integrating Bulk SMS with APIs
For businesses aiming to automate their SMS communication and streamline customer interactions, integrating bulk SMS with their existing systems via APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is a game-changer. SMS APIs allow businesses to seamlessly send messages, schedule campaigns, manage replies, and retrieve delivery reports directly from their applications or CRM systems. Here’s a closer look at how SMS APIs work, common methods, and best practices for integration.
1. What is an SMS API?
An SMS API is a programming interface that connects business applications with SMS gateways, enabling automated SMS sending and management. Using an SMS API, businesses can integrate SMS functionality directly into their software, websites, mobile apps, or CRM systems, allowing them to control SMS communication from within their own platforms. This integration simplifies workflows, improves efficiency, and provides a consistent, cohesive experience for customers.
2. Common SMS API Functions
An SMS API offers several useful functions that make it easy to manage SMS communication:
- Send SMS: This is the core function, enabling businesses to trigger SMS sends for individual messages or bulk campaigns.
- Schedule Messages: With this function, businesses can set a specific date and time for messages to be sent. Scheduling is ideal for time-sensitive campaigns, reminders, or follow-up messages.
- Fetch Delivery Reports: The API can retrieve real-time delivery statuses, providing data on whether messages have been successfully delivered, failed, or are pending.
- Manage Two-Way SMS: Two-way SMS support allows businesses to receive and process replies. This function is valuable for customer feedback, appointment confirmations, or quick response campaigns.
- Create and Use Templates: Some SMS APIs enable businesses to create templates for commonly used messages, streamlining communication by minimising the need for repeated message creation.
By leveraging these functions, businesses can automate and optimise their SMS campaigns, creating a seamless experience for both internal teams and customers.
3. Benefits of Using an SMS API
Integrating SMS functionality with an API provides several distinct benefits for businesses:
- Automation: SMS APIs enable automated workflows, reducing the need for manual intervention. For instance, an e-commerce store can automatically send an SMS confirmation every time a customer places an order.
- Customisation: APIs allow businesses to personalise messages based on customer data, such as names, preferences, and purchase history, ensuring that messages are relevant and engaging.
- Real-Time Updates: Delivery reports and status codes are accessible in real time, allowing businesses to monitor performance and take immediate action if issues arise.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, SMS APIs scale to meet increasing demand, ensuring that companies can reach larger audiences without compromising on speed or performance.
- Enhanced Security: Many SMS APIs support security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA) and token-based authentication, which help safeguard customer data and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
4. Popular API Methods and Their Use Cases
The versatility of SMS APIs means businesses can use them for a variety of use cases. Here are some of the most common API methods and examples of how they can be applied:
- Transactional Notifications: With APIs, businesses can automatically send transactional messages, such as order confirmations, shipping updates, and appointment reminders. This provides customers with timely updates and reduces inquiries.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For platforms requiring secure login, SMS APIs make it easy to integrate 2FA, sending one-time passcodes (OTPs) to verify users. This is commonly used in finance, e-commerce, and health industries to protect sensitive information.
- Marketing Campaigns: Using an API, businesses can trigger SMS campaigns for promotions, flash sales, and other marketing initiatives directly from their CRM. By setting specific triggers, like a customer's birthday or anniversary, businesses can send personalised offers that feel timely and relevant.
- Customer Support and Service Updates: SMS APIs allow support teams to send real-time updates to customers, such as ticket confirmations, wait time notifications, or follow-ups after a service interaction. This keeps customers informed and enhances their experience with the brand.
- Event Reminders and Invitations: For event organisers, SMS APIs simplify the process of sending reminders and updates. From initial invitations to last-minute location changes, SMS can keep attendees up-to-date in real time.
5. Best Practices for SMS API Integration
To get the most out of an SMS API, businesses should follow a few best practices:
- Plan for Rate Limits and Throttling: High-volume SMS campaigns can hit rate limits if not properly managed. Many providers use throttling to control message flow and ensure delivery. Businesses should plan their API usage around these limits to avoid message delays.
- Use Webhooks for Real-Time Updates: Webhooks provide a way to receive notifications about events (like message delivery) without needing to repeatedly check the API. For example, a webhook can notify the business as soon as a message is delivered, making it easy to track campaign performance in real time.
- Monitor and Analyse Delivery Reports: API delivery reports offer valuable insights into message success rates. Analysing these reports can reveal trends in failed messages, helping businesses improve data quality and troubleshoot issues, like incorrect numbers or network issues.
- Ensure Security and Compliance: When using SMS APIs, businesses must follow privacy and security standards, especially when handling personal data. Use encryption, token-based authentication, and API keys to keep data secure and comply with Australia’s Privacy Act 1988 and other relevant regulations.
- Test Before Launch: Testing SMS functionality before launching a full campaign is crucial. This includes checking character limits, testing message templates, and verifying personalisation tokens to ensure messages display correctly. Testing also helps confirm that API requests are set up correctly and will work smoothly in real-time scenarios.
6. Selecting the Right SMS API Provider
Not all SMS APIs are created equal, and choosing the right provider can make a big difference in performance, ease of use, and customer satisfaction. When evaluating an SMS API provider, consider the following:
- Reliability and Delivery Speed: Choose a provider with a strong record of high delivery rates and low latency. For time-sensitive messages, such as 2FA or alerts, reliable and fast delivery is essential.
- Global Reach and Local Expertise: If your business communicates internationally, look for a provider with extensive carrier connections. For Australian businesses, local expertise is also beneficial for navigating compliance with the Spam Act 2003 and other local regulations.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your SMS needs may increase. Select a provider that can scale with your business, offering flexible plans and high-volume support when needed.
- Integration Support: Some providers offer SDKs (Software Development Kits) and sample code to make integration easier. Look for a provider with comprehensive documentation and support to help you set up and troubleshoot your API integration.
- Cost and Pricing Flexibility: API pricing can vary significantly between providers. Consider both upfront costs and per-message fees, and choose a provider whose pricing model aligns with your budget and projected message volume.
7. Real-Life Example of SMS API Integration
Imagine an Australian e-commerce business that wants to improve its post-purchase communication. By integrating an SMS API with its order management system, the business can automatically send personalised SMS updates for each step of the fulfilment process—from order confirmation to dispatch and delivery.
Here’s how it works:
- Order Confirmation: When a customer places an order, an API call triggers an SMS confirmation, thanking them and providing a summary of their order.
- Dispatch Notification: When the order is packed and ready to ship, another API call sends an SMS with a tracking link, keeping the customer updated in real time.
- Delivery Confirmation: Once the order is delivered, the final API call sends a thank-you message, along with a request for feedback.
This seamless communication keeps customers informed at every stage, reduces support inquiries, and enhances the overall customer experience.
Security and Privacy in Bulk SMS
As businesses increasingly rely on bulk SMS to communicate with customers, security and privacy become essential considerations. In Australia, data privacy laws, particularly the Privacy Act 1988, outline strict guidelines for how businesses must handle personal information. Bulk SMS providers and users alike are responsible for safeguarding data and ensuring that their communications are compliant. Here’s a look at the key security measures, privacy concerns, and best practices for using bulk SMS safely and responsibly.
1. Data Protection Standards
Protecting customer data is crucial for any business that uses bulk SMS. Reputable SMS providers adhere to high data protection standards, often employing encryption, secure storage, and access control measures to safeguard personal information. Key data protection strategies include:
- Encryption: Data encryption ensures that information is securely transmitted from one system to another. By encrypting SMS messages in transit, businesses reduce the risk of interception by unauthorised parties.
- Secure Data Storage: Many SMS providers store customer data on secure servers with restricted access. This includes sensitive information like phone numbers, names, and any other data associated with SMS messages.
- Access Control: Limiting access to SMS platforms and customer data to only essential personnel is an effective security practice. Many platforms use role-based access control to manage permissions and minimise data exposure.
2. API Security
For businesses using SMS APIs to automate messaging, securing API access is critical. API security involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorised use and data breaches. Key security practices for SMS APIs include:
- API Keys and Authentication: SMS providers typically use API keys or token-based authentication to restrict access. Businesses should manage and protect these keys carefully, treating them like passwords and never exposing them in public or shared code repositories.
- IP Whitelisting: Some providers offer IP whitelisting, allowing businesses to specify which IP addresses are authorised to use their SMS API. This adds an extra layer of security by restricting access to trusted networks.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: Rate limiting helps prevent abuse of the SMS API by capping the number of requests within a given time period. This can mitigate risks from excessive or malicious requests, preserving API availability and system stability.
3. Compliance with Australian Privacy Laws
In Australia, businesses that handle customer data must comply with the Privacy Act 1988 and adhere to the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). These laws are designed to protect individuals' personal information and ensure transparency in how data is collected, used, and stored. For SMS campaigns, compliance involves:
- Obtaining Consent: Consent is a fundamental requirement for sending commercial SMS messages in Australia. Before initiating any SMS campaign, businesses must obtain explicit consent from recipients, either through an opt-in form, registration process, or customer interaction.
- Providing Opt-Out Options: The Spam Act 2003 requires that all marketing messages include a way for recipients to opt out. SMS messages should contain simple opt-out instructions, like “Reply STOP to unsubscribe.” This ensures that recipients have control over their preferences and can easily unsubscribe if desired.
- Limiting Data Collection: Businesses should collect only the information necessary for their SMS campaigns. Over-collecting data increases risk and goes against the principles of data minimisation under the Privacy Act.
- Transparency and Disclosure: Under the APPs, businesses must inform customers how their data will be used, stored, and shared. Privacy policies should be readily accessible, explaining the purpose of data collection and how to contact the business with any questions or concerns.
4. Managing and Protecting Customer Data
Effective data management is essential for safeguarding customer privacy and ensuring that personal information remains secure. Businesses can implement several best practices for data management in bulk SMS:
- Data Retention Policies: Define clear retention policies that specify how long customer data will be stored and when it will be deleted. Retaining data longer than necessary increases risk, so businesses should regularly review and delete outdated information.
- Data Anonymisation: If the SMS campaign does not require personally identifiable information (PII), consider anonymising customer data. For example, anonymising data for analytics or reporting purposes can help protect privacy while still allowing businesses to gather insights.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help identify and address potential security gaps. Audits ensure that security protocols are up to date and that any new risks are promptly mitigated.
5. Using Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for Secure Access
Many SMS platforms and APIs offer two-factor authentication (2FA) to provide an additional layer of security. By requiring both a password and a one-time code (often sent via SMS), 2FA helps prevent unauthorised access, even if passwords are compromised. This is particularly valuable for businesses handling sensitive customer information, as it ensures only authorised personnel can access the SMS platform.
6. Preventing SMS Fraud and Spoofing
SMS fraud and spoofing involve sending deceptive messages that appear to come from a trusted source to trick recipients into disclosing sensitive information or clicking malicious links. To protect against these risks, businesses should:
- Use Verified Sender IDs: Using an alphanumeric or verified sender ID helps recipients identify the business, adding credibility and trust. Verified sender IDs are less likely to be spoofed and make it clear to customers that the message is legitimate.
- Educate Customers: Inform customers about common SMS scams and encourage them to report suspicious messages. Educated customers are less likely to fall victim to phishing attempts and other forms of SMS fraud.
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Regularly monitor SMS traffic for any unusual patterns, such as high volumes of messages sent in a short period. This can help detect fraudulent activity early and allow businesses to take corrective action before it escalates.
7. Best Practices for SMS Privacy and Security Compliance
To maintain security and privacy in bulk SMS campaigns, businesses should implement the following best practices:
- Use Secure, Reputable Providers: Partner with SMS providers who prioritise data security and comply with industry standards. Reputable providers invest in secure infrastructure, follow best practices, and adhere to data protection laws.
- Regularly Update Security Protocols: Cybersecurity is constantly evolving, and security protocols should be updated to stay ahead of new threats. This includes regularly updating passwords, API keys, and access credentials.
- Provide Clear Opt-In/Opt-Out Procedures: Make it easy for customers to opt in and out of SMS communications. This builds trust and ensures compliance with privacy laws.
- Document Privacy Policies: Clearly outline your privacy policies and make them accessible to customers. Transparency builds customer confidence and demonstrates a commitment to responsible data handling.
- Respond Promptly to Privacy Concerns: Customers may have questions about how their data is used or request modifications to their preferences. Train customer support teams to handle these inquiries efficiently, as a timely response can reinforce trust and loyalty.
Best Practices for Effective Bulk SMS Campaigns
Bulk SMS is a powerful tool, but using it effectively requires a well-planned approach. To maximise engagement, ensure compliance, and make the most of your messaging, consider these best practices for creating impactful bulk SMS campaigns.
1. Craft Clear and Concise Messages
SMS messages have a character limit (typically 160 characters with GSM encoding), so it’s essential to keep your message direct and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details and focus on delivering a clear, actionable message that communicates your intent immediately.
- Example: Instead of “Hello, valued customer! We are excited to let you know that we’re having a special sale this weekend with discounts on many of our products,” try “This weekend only: 20% off storewide. Visit us in-store or online. Don’t miss out!”
2. Personalise Your Messages
Personalisation helps increase engagement by making messages feel relevant and targeted. Include details like the customer’s name, past purchases, or location if appropriate. Personalised SMS messages show customers that you’re not sending a one-size-fits-all message, which can make a significant difference in response rates.
- Example: “Hi Sarah, enjoy 10% off your next order with code SARAH10. Thanks for being a loyal customer!”
3. Use a Strong Call-to-Action (CTA)
A clear call-to-action encourages customers to take the next step, whether it’s visiting your website, redeeming a discount, or confirming an appointment. Make sure your CTA is easy to understand and stands out within the message.
- Examples of Effective CTAs:
- “Shop now at [link]”
- “Reply YES to confirm”
- “Show this SMS for a 15% discount in-store”
4. Send Messages at the Right Time
Timing can significantly impact the effectiveness of SMS campaigns. Sending messages too early or too late may annoy recipients, leading to a higher opt-out rate. Research your audience and use data to identify the optimal times for engagement. For instance, mid-morning and early afternoon are often good times to reach customers without being intrusive.
- Tip for Australian Businesses: Consider time zone differences across the country, especially if your customer base spans multiple states. SMS scheduling tools can help you manage this.
5. Segment Your Audience
Segmenting your audience allows you to send more targeted messages based on factors like customer behaviour, location, purchase history, or demographics. By sending relevant messages to specific groups, you improve engagement and make customers feel valued.
- Examples of Segmentation:
- Geographical: Send location-specific promotions to customers in particular areas.
- Behavioural: Send reminders to customers who have items in their cart but haven’t completed the purchase.
- Transactional: Follow up with customers after a recent purchase with related product recommendations.
6. Respect Frequency and Avoid Message Fatigue
Sending too many messages can lead to customer fatigue and increase the likelihood of opt-outs. Determine an appropriate frequency for your SMS campaigns based on customer engagement data and industry norms. For many businesses, once or twice a week is effective, but this can vary depending on the nature of the business and the type of messages.
- Tip: Track opt-out rates and engagement levels to identify if you’re messaging too frequently. Adjust your frequency as needed to keep customers engaged without overwhelming them.
7. Include an Easy Opt-Out Option
To comply with the Spam Act 2003 in Australia, all marketing SMS messages must include an easy way for customers to opt out. Use simple instructions, such as “Reply STOP to unsubscribe.” Making the opt-out process straightforward not only keeps you compliant but also builds trust with your audience.
8. A/B Test Your Campaigns
A/B testing allows you to experiment with different message formats, CTAs, and timing to see what resonates best with your audience. Test elements like message length, tone, personalisation, or CTA wording to determine which version yields higher engagement and conversions.
- Example: Test a short message with a direct CTA (“20% off today only. Shop now!”) against a slightly longer, more descriptive version (“Exclusive deal! Get 20% off today only at [link]. Limited time!”) to see which performs better.
9. Leverage Automation and Scheduling
Using automation and scheduling features within your SMS platform can streamline your campaigns and ensure messages reach recipients at optimal times. Automation is particularly helpful for recurring messages like birthday offers, appointment reminders, and follow-ups.
- Example of Automation: Set up automated SMS messages for abandoned cart reminders. If a customer leaves items in their cart without checking out, an automated SMS can be sent after a specified period, encouraging them to complete the purchase.
10. Track and Analyse Campaign Performance
To understand the success of your SMS campaigns, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as open rates, click-through rates (if using links), opt-out rates, and conversion rates. Analysing this data provides insights into what’s working and where there’s room for improvement, allowing you to refine future campaigns for better results.
- Important Metrics to Track:
- Delivery Rate: Ensures your messages are reaching recipients.
- Response Rate: Measures customer engagement, particularly for interactive campaigns.
- Conversion Rate: Tracks how many recipients complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or booking an appointment.
11. Optimise for Mobile Links
If your SMS includes a link to your website or landing page, make sure it’s mobile-friendly. Since recipients are reading the message on their phones, a poorly optimised landing page can lead to a frustrating experience and lost conversions. Test the linked content on various devices to ensure it loads quickly and is easy to navigate.
- Tip: Use URL shorteners to keep links brief and tidy, saving valuable character space and making the message appear cleaner.
12. Ensure Compliance with Australian Regulations
Compliance with local laws, including the Spam Act 2003, is essential for bulk SMS marketing. In addition to providing opt-out options, make sure you have explicit consent from recipients before sending messages. Following these rules not only protects your business from penalties but also strengthens customer trust and brand reputation.
13. Monitor and Reduce Bounce Rates
A high bounce rate (failed message delivery) can indicate issues with your contact list, such as outdated phone numbers or incorrect data. Regularly audit and clean your list to remove invalid numbers, which helps improve delivery rates, reduces costs, and maintains a positive sender reputation.
14. Use Dynamic Fields for Personalisation
Most bulk SMS platforms support dynamic fields, allowing you to personalise messages by automatically inserting recipient-specific information, such as their name, location, or recent purchases. Dynamic fields create a personalised experience without the need for manual message customisation, making it easier to scale while maintaining relevance.
- Example: “Hi [First Name], thanks for your recent purchase! Use code WELCOME10 for 10% off your next order.”
Understanding Australian Regulations
For businesses using bulk SMS, compliance with Australian regulations is essential to ensure ethical practices and protect customer trust. Australia’s legal landscape for SMS marketing primarily revolves around the Spam Act 2003, enforced by the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA). Understanding and adhering to these regulations helps businesses avoid legal issues, preserve their reputation, and build positive relationships with customers. Here’s what Australian businesses need to know to keep their SMS campaigns compliant.
1. The Spam Act 2003
The Spam Act 2003 is the cornerstone of Australian legislation governing electronic communications, including SMS. The Act aims to protect consumers from unwanted marketing messages by setting strict rules around consent, identification, and opt-out requirements. Businesses must comply with the Act when sending any commercial SMS message. Key aspects of the Spam Act include:
- Consent: Businesses must obtain clear and explicit consent from recipients before sending them marketing messages. Consent can be either express (e.g., when a customer opts in to receive messages) or inferred through a prior business relationship.
- Identification: Every SMS message must clearly identify the sender. This could be the business name or a registered trading name, ensuring recipients know who the message is from.
- Unsubscribe Mechanism: All commercial SMS messages must include an easy way for recipients to opt out. This usually involves a simple “Reply STOP” instruction, allowing customers to unsubscribe without hassle.
Non-compliance with the Spam Act can result in substantial penalties, including fines. Businesses are encouraged to familiarise themselves with the full details of the Spam Act 2003 to understand their obligations.
2. Types of Consent: Express vs. Inferred
Consent is central to the Spam Act, and businesses need to understand the difference between express and inferred consent:
- Express Consent: This is the most straightforward form of consent. It is given explicitly by the customer, typically when they sign up for marketing messages or select an opt-in box. Express consent is clear, documented, and remains valid until the customer decides to opt out.
- Inferred Consent: Inferred consent applies in situations where there is an existing business relationship, and it would be reasonable to assume the customer is interested in receiving marketing messages. For example, if a customer has recently purchased from the business, inferred consent may apply. However, inferred consent is more context-dependent, and businesses should use it cautiously to avoid overstepping privacy boundaries.
3. Identification Requirements
To ensure transparency, the Spam Act requires all commercial SMS messages to identify the sender. This means that the SMS must include either the business name or an easily recognisable identifier. Using a registered trading name is generally best practice, as it provides clarity to recipients. Alphanumeric sender IDs are often used for this purpose, as they allow businesses to display their brand name rather than a random number.
Clear identification builds trust with recipients, letting them know that the message is from a legitimate source. It also reduces the risk of recipients reporting messages as spam, which can harm the business’s sender reputation and affect deliverability.
4. The Importance of an Opt-Out Mechanism
An unsubscribe, or opt-out mechanism, is a critical component of any SMS marketing campaign. Under Australian law, every SMS message must include a simple and functional opt-out option. Most businesses accomplish this by instructing recipients to reply with “STOP” to unsubscribe. Once a customer has opted out, businesses must respect their choice and ensure no further marketing messages are sent to that number.
To stay compliant and maintain positive customer relationships, businesses should:
- Implement Automated Opt-Outs: Many SMS platforms offer automated opt-out functions, which instantly remove customers from the messaging list upon receiving a “STOP” reply. This prevents any accidental sending of further messages.
- Monitor and Manage Opt-Out Requests: Regularly review your SMS platform to ensure that opt-out requests are properly recorded and actioned. Failing to honour opt-out requests can lead to penalties and damage customer trust.
5. Privacy Act 1988 and the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs)
In addition to the Spam Act, the Privacy Act 1988 and the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) regulate how businesses collect, store, and use personal information. For SMS campaigns, the Privacy Act requires that customer data (such as phone numbers and names) is handled securely and used only for the purpose for which it was collected.
Key requirements under the Privacy Act and APPs include:
- Data Collection and Use: Collect only the information needed for SMS campaigns, and make sure customers understand how their data will be used.
- Data Security: Protect personal data against unauthorised access, loss, or misuse. SMS platforms with strong data security protocols help businesses comply with these requirements.
- Access and Correction Rights: Customers have the right to access the information held about them and request corrections if it is inaccurate. Businesses should have a clear process in place for handling such requests.
6. Record-Keeping and Consent Management
Keeping records of customer consent is an essential part of compliance. Whether consent is express or inferred, maintaining documentation helps protect businesses in case of a complaint or audit. Many SMS platforms offer built-in consent management features, which make it easy to track when and how consent was obtained.
Best Practices for Consent Management:
- Timestamped Records: Record the date and time of consent to demonstrate compliance if needed.
- Opt-In Language: Save the specific opt-in wording customers agreed to, as it shows that consent was obtained in a clear and transparent manner.
- Regular Audits: Periodically audit your consent records to ensure they are up to date and accurately reflect your customer database.
7. Handling Complaints and Compliance Checks
If a customer files a complaint or ACMA conducts a compliance check, it’s crucial to respond promptly and cooperatively. ACMA has the authority to investigate complaints related to SMS marketing, and businesses are required to demonstrate compliance. To prepare for possible compliance checks:
- Establish Internal Policies: Have a documented set of policies for handling complaints and compliance inquiries, detailing steps for investigating and resolving issues.
- Keep Accurate Records: Retain records of consent, opt-out requests, and campaign details in case they are needed for a compliance review.
- Respond Promptly to Complaints: If a customer raises a concern about your SMS practices, address it swiftly to demonstrate your commitment to responsible marketing and compliance.
8. Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with Australian SMS regulations can result in significant penalties. ACMA has the power to issue fines, enforce undertakings, and take court action against businesses that breach the Spam Act or Privacy Act. Penalties for SMS non-compliance include:
- Fines: ACMA can impose penalties, with fines based on the severity of the breach and the size of the business.
- Enforceable Undertakings: Businesses may be required to enter enforceable undertakings, where they commit to specific compliance actions to prevent future breaches.
- Public Naming: In some cases, ACMA may publicly name businesses that fail to comply, impacting brand reputation and customer trust.
By understanding these potential consequences, businesses can appreciate the importance of adhering to regulations and maintaining best practices in SMS marketing.
9. Staying Informed of Regulatory Updates
Australia’s privacy and spam regulations evolve as technology and consumer expectations change. Businesses are responsible for keeping up to date with any changes to the Spam Act, Privacy Act, and APPs to ensure ongoing compliance. Regularly reviewing ACMA’s website, consulting with legal advisors, and staying informed about industry best practices can help businesses navigate regulatory requirements and avoid unintentional breaches.
Choosing a Bulk SMS Provider in Australia
Selecting the right bulk SMS provider is a critical step for businesses aiming to maximise the effectiveness of their SMS campaigns. With numerous providers offering different features, pricing models, and levels of customer support, it’s essential to choose a provider that aligns with your business goals and meets the needs of your audience. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a bulk SMS provider in Australia.
1. Local Expertise and Compliance Support
Australia’s regulatory landscape for SMS is specific, with requirements under the Spam Act 2003 and the Privacy Act 1988. Working with a provider that has local expertise and understands these regulations can simplify compliance and reduce the risk of penalties. A provider familiar with the Australian market can also offer insights into optimal messaging practices, timing, and engagement strategies that resonate with local audiences.
- Compliance Features: Look for a provider that offers built-in tools for compliance, such as automated opt-out management, consent tracking, and options for personalising sender IDs.
2. High Delivery Rates and Speed
One of the primary advantages of SMS is its immediacy, so it’s essential to choose a provider with high delivery rates and fast message transmission. Delivery rates indicate the percentage of messages successfully delivered to recipients, while speed ensures that messages reach recipients within seconds, which is especially important for time-sensitive communications like sales alerts or two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Delivery Success: Ask potential providers about their average delivery success rates and the measures they take to ensure messages reach recipients.
- Latency: Some providers offer premium or priority routes for faster delivery, which can be beneficial for urgent messages.
3. Reliable API and Integration Capabilities
For businesses looking to integrate SMS functionality into their existing systems, a reliable SMS API is essential. The SMS API allows for automation and customisation, enabling businesses to send messages directly from their CRM, e-commerce platform, or customer support system.
- Supported Integrations: Ensure that the provider’s API can integrate smoothly with the tools and software your business already uses.
- Documentation and Developer Support: Look for a provider with comprehensive API documentation and robust support for developers, making it easier to set up, test, and manage the integration.
4. Transparent Pricing and Flexible Plans
SMS pricing models can vary significantly, so it’s important to choose a provider that offers transparent and flexible pricing to suit your budget. Most providers charge per SMS, but discounts may apply for higher volumes. Additionally, some providers offer monthly plans or packages with set allotments, which can be more economical for businesses with regular messaging needs.
- Pay-as-You-Go vs. Subscription: Determine whether pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing makes more sense for your business.
- Additional Fees: Be aware of any hidden fees, such as charges for premium routes, sender ID customisation, or delivery receipts. Look for a provider with clear pricing that won’t surprise you with unexpected costs.
5. Customer Support and Onboarding Assistance
When choosing an SMS provider, customer support quality can make a big difference, particularly during setup or if issues arise with delivery. Look for a provider with responsive, knowledgeable support teams available in Australian time zones. Many providers also offer onboarding assistance, which can help ensure your campaigns are set up correctly and optimised for success.
- Support Channels: Check whether the provider offers support via phone, email, or live chat, and confirm their availability hours to ensure they align with your business needs.
- Onboarding Services: Some providers offer onboarding sessions or training resources, which can be particularly valuable for businesses new to SMS marketing.
6. Compliance and Security Measures
SMS campaigns involve handling customer data, so choosing a provider with robust compliance and security protocols is essential. This includes data encryption, secure data storage, and adherence to Australian privacy laws. Providers should also offer tools to help businesses stay compliant, such as opt-out management and consent tracking.
- Data Protection: Confirm that the provider encrypts data during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorised access.
- Compliance Tools: Look for features like automated opt-out handling and consent verification, which simplify compliance with Australian regulations.
7. Analytics and Reporting Capabilities
To understand the effectiveness of your SMS campaigns, detailed analytics and reporting tools are essential. These tools help you track delivery rates, response rates, and other key metrics, providing insights into campaign performance and areas for improvement.
- Real-Time Reports: Some providers offer real-time reporting, which allows you to monitor campaign performance as messages are delivered.
- Detailed Metrics: Look for a provider that offers metrics on delivery rates, open rates, click-through rates (if using links), opt-outs, and conversions. Advanced reporting capabilities allow you to gain deeper insights and refine future campaigns.
8. Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, your SMS needs may increase as well. Choose a provider that can scale with you, whether you’re sending a few thousand messages a month or millions. A scalable provider will be able to accommodate your needs as they evolve, without compromising delivery quality or speed.
- High-Volume Messaging: Ask providers about their capacity for high-volume messaging and any restrictions that might affect large campaigns.
- Flexible Options: Look for a provider with a range of options, such as API integrations, campaign scheduling, and segmentation tools, to support different types of SMS marketing as your strategy matures.
9. Sender ID and Customisation Options
Customising the sender ID (the name or number that appears as the sender) can enhance brand recognition and encourage engagement. Many providers offer alphanumeric sender IDs, which allow businesses to use their brand name instead of a generic number. Custom sender IDs are particularly useful for promotional messages, as they make it immediately clear who the message is from.
- Alphanumeric Sender IDs: Check if the provider supports alphanumeric sender IDs, which can be more memorable for recipients.
- Message Personalisation: Some providers offer advanced personalisation options, allowing you to insert dynamic fields like customer names, locations, or recent purchases to make each message more relevant.
10. Trial Period or Free Credits
Before committing to a provider, it can be helpful to test the service through a trial period or free credits. Many SMS providers offer trial options that allow you to explore their platform’s functionality, test delivery rates, and assess the quality of customer support.
- Free Trial or Demo: A trial period or demo account allows you to experiment with the platform and see if it meets your needs.
- Test Campaigns: Use the trial period to run test campaigns, send messages to different devices, and evaluate delivery times and message quality.
Advanced Features and Future Trends in Bulk SMS
Bulk SMS has evolved significantly from simple text-based communication to a sophisticated, data-driven marketing tool. With advancements in technology and growing customer expectations, SMS providers now offer a range of advanced features that enhance campaign effectiveness and personalisation. Additionally, emerging trends hint at what the future holds for SMS marketing. Here are some of the top features and trends to watch for:
1. Rich Communication Services (RCS)
- What It Is: RCS is the next generation of SMS technology, bringing multimedia capabilities to traditional text messaging. Sometimes referred to as “SMS 2.0,” RCS allows brands to include images, videos, buttons, and even carousels in their messages.
- Benefits: RCS makes SMS more interactive and visually engaging, enhancing the customer experience. It can boost engagement by allowing recipients to view images of products, watch short videos, or navigate options directly within the message.
- Current Adoption: While RCS is gaining traction globally, adoption varies by carrier and device. Australian businesses may benefit from testing RCS campaigns as its availability expands.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning for Personalisation
- What It Is: AI and machine learning allow SMS platforms to analyse customer data and make real-time decisions on message content, timing, and segmentation.
- Benefits: AI-powered personalisation means businesses can send messages that are highly relevant to individual customers, such as product recommendations based on past purchases or predictive offers that anticipate customer needs.
- Current Applications: Some SMS providers offer AI-driven tools that recommend send times, craft personalised messages, or predict customer engagement based on historical data.
3. SMS Chatbots and Two-Way Messaging
- What It Is: SMS chatbots are automated systems that can hold two-way conversations with customers, answering questions, processing requests, and gathering information.
- Benefits: With SMS chatbots, businesses can offer immediate responses and customer service around the clock, improving the customer experience without needing human intervention.
- Popular Use Cases: Chatbots are effective for customer service inquiries, appointment scheduling, order tracking, and frequently asked questions. They offer a more conversational experience that can build stronger customer relationships.
4. Advanced Analytics and Predictive Analytics
- What It Is: Advanced analytics go beyond basic delivery and response metrics, offering insights into user behaviour, campaign trends, and customer segments. Predictive analytics uses past data to forecast future behaviour, such as likely purchase times or engagement levels.
- Benefits: These tools allow businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimise campaigns, and improve targeting by understanding what works and what doesn’t.
- In Practice: Australian businesses using predictive analytics can anticipate high-demand periods and tailor messages accordingly, boosting conversions by reaching customers at the right time.
5. Enhanced Security with SMS for Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- What It Is: Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security feature that adds an extra layer of protection to customer accounts, requiring a second form of identification (usually a one-time code sent via SMS) in addition to a password.
- Benefits: 2FA improves account security, builds trust with customers, and helps protect sensitive information. It is particularly valuable for sectors like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, where security is paramount.
- Future of 2FA: As cyber threats evolve, SMS will likely remain a popular choice for 2FA due to its simplicity and effectiveness, though it may be supplemented by biometric or app-based options in the future.
6. Integration with CRM and Marketing Automation Platforms
- What It Is: Many SMS providers now integrate directly with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and marketing automation platforms, allowing businesses to manage SMS campaigns within their existing tools.
- Benefits: Integrated SMS campaigns can leverage customer data stored in the CRM, enabling highly personalised messages, automated workflows, and seamless customer journey management.
- How It’s Used: By connecting SMS with CRM, businesses can automate follow-up messages, segment audiences based on behaviour, and sync SMS with other marketing channels like email for an omnichannel approach.
7. Dynamic Fields and Hyper-Personalisation
- What It Is: Dynamic fields allow businesses to insert individualised details (e.g., name, location, recent purchases) directly into SMS messages, creating a hyper-personalised experience.
- Benefits: Hyper-personalisation can increase engagement by making messages feel more relevant and tailored to the recipient.
- In Action: For example, a retailer might send a dynamic message that includes a customer’s name and recent product views, boosting the likelihood of a conversion.
8. SMS for Payment Reminders and Mobile Payments
- What It Is: SMS payment reminders notify customers of upcoming or overdue payments, while SMS-based mobile payment options enable secure transactions directly from the message.
- Benefits: SMS payment features make it easy for customers to complete payments with minimal friction, improving cash flow for businesses.
- Future Prospects: As mobile payments gain traction, SMS may become an increasingly important tool for frictionless, secure payments, particularly in industries like finance, utilities, and e-commerce.
9. Geo-Targeting for Location-Based Campaigns
- What It Is: Geo-targeting allows businesses to send SMS messages to recipients in specific locations. By leveraging GPS or cell tower data, businesses can target customers in real-time based on their physical location.
- Benefits: Geo-targeting is ideal for location-specific offers, such as restaurant discounts, event invitations, or in-store promotions, making it highly relevant and actionable.
- Example Use Case: A retail chain might send a special offer to customers located within a certain radius of one of their stores, encouraging foot traffic with a limited-time promotion.
10. Integration with Rich Media Elements and MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service)
- What It Is: MMS enables businesses to send images, audio, and short videos in their messages. While MMS isn’t as widely used as SMS, it provides a visually rich experience that can enhance engagement.
- Benefits: MMS is highly engaging and can help products stand out with visuals, which is especially effective for retail, hospitality, and entertainment industries.
- Emerging Trend: As mobile device capabilities expand, MMS may see greater adoption as part of mixed media campaigns, particularly among businesses seeking to create a more immersive brand experience.
11. API Enhancements for Greater Flexibility
- What It Is: Advanced SMS APIs now offer more features, such as multi-language support, customisable delivery settings, and options for complex automation.
- Benefits: Enhanced API features allow businesses to build highly customised and scalable SMS campaigns, making it easier to manage large-scale campaigns and automate workflows.
- In Practice: With API flexibility, businesses can customise message timing, select priority routes for critical messages, or segment audiences dynamically, all from within their systems.
Measuring ROI and Analytics in Bulk SMS
To understand the effectiveness of bulk SMS campaigns, businesses need to track key metrics and analyse data that provides insights into customer engagement, conversions, and overall return on investment (ROI). Unlike traditional marketing channels, SMS analytics offer quick, actionable data that helps businesses make real-time adjustments. Here’s a guide to the most critical metrics, tools, and strategies for measuring the success of your SMS campaigns.
1. Key Metrics for Tracking SMS Campaign Performance
Measuring the performance of bulk SMS campaigns requires focusing on metrics that reveal engagement, reach, and effectiveness. Here are some of the essential metrics to consider:
- Delivery Rate: The percentage of messages successfully delivered to recipients. A high delivery rate indicates a clean, accurate contact list, while a lower rate could suggest outdated or incorrect numbers.
- Open Rate: Although SMS open rates are typically high (over 90%), tracking open rates where possible helps confirm that recipients are viewing your messages. Most SMS platforms don’t track opens like email, but quick response times can indirectly indicate high engagement.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): For SMS messages that include links, the CTR shows the percentage of recipients who clicked the link. This metric is valuable for tracking the effectiveness of promotions, landing pages, and call-to-action (CTA) buttons.
- Conversion Rate: This metric measures the percentage of recipients who completed a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form, after clicking a link in the SMS. Conversion rates offer direct insight into the campaign’s success in driving customer action.
- Response Rate: If the campaign encourages replies (e.g., “Reply YES to confirm”), the response rate shows how many recipients engaged with the message. Higher response rates suggest that recipients find the message relevant and are willing to interact.
- Opt-Out Rate: This metric indicates how many recipients chose to unsubscribe from your SMS list after receiving a message. A high opt-out rate can signal that the message frequency or content is not resonating with your audience.
2. Calculating ROI for Bulk SMS Campaigns
The ROI calculation for bulk SMS is straightforward and can be highly valuable for assessing the financial impact of your campaigns. To calculate ROI, use the following formula:
ROI (%) = [(Total Revenue from SMS Campaign - Total Cost of SMS Campaign) / Total Cost of SMS Campaign] x 100
- Example Calculation: Suppose an SMS campaign generated $5,000 in sales and cost $500 to execute. The ROI would be:
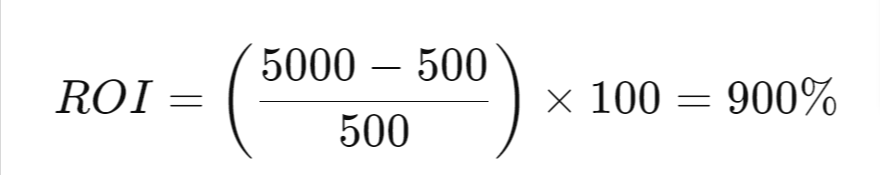
- This means the campaign yielded a 900% return, demonstrating a strong ROI.
Calculating ROI helps businesses justify their SMS spend and identify the most profitable types of campaigns, which can guide future marketing decisions.
3. Using A/B Testing for Optimisation
A/B testing (or split testing) is a valuable strategy for improving SMS campaign effectiveness. By sending two versions of a message to small groups of your audience, you can test different variables and determine which version performs better. Elements to test include:
- Message Content: Test different wording, tone, or phrasing to see what resonates most with recipients.
- Timing: Experiment with sending messages at different times of day to identify when your audience is most responsive.
- CTA: Try different CTAs to see which drives the highest engagement, such as “Shop Now” vs. “Learn More.”
After testing, implement the winning version across the full campaign to maximise engagement and conversions. Regular A/B testing can improve overall SMS performance by continuously refining messaging.
4. Leveraging Delivery Reports for Real-Time Insights
Delivery reports offer valuable, real-time data on the status of each message sent, providing insights into successful deliveries, failures, and pending messages. Monitoring delivery reports can help identify issues in your SMS campaign, such as network errors or invalid numbers, allowing you to make adjustments quickly.
- Successful Delivery: A high rate of successful deliveries indicates your contact list is up-to-date and your messages are reaching recipients.
- Failed Messages: Messages can fail for various reasons, including invalid numbers or network issues. Regularly reviewing failed messages helps identify and remove invalid contacts, keeping your list clean and improving future delivery rates.
By understanding delivery trends, businesses can improve data quality, reduce costs associated with undeliverable messages, and ensure that campaigns are reaching their intended audience.
5. Analysing Engagement Through Click-Through and Conversion Rates
For campaigns that include links (e.g., promotions, product launches, surveys), click-through and conversion rates are critical indicators of customer engagement. Here’s how to interpret these metrics:
- Click-Through Rate: A high CTR indicates that your message content and CTA are compelling enough to drive action. If CTR is low, consider testing new language, stronger CTAs, or more targeted messaging.
- Conversion Rate: Conversion rates show how effective your SMS campaign is at driving the desired action. For example, if your campaign aims to boost sales, the conversion rate will reveal the percentage of recipients who made a purchase after clicking the SMS link. Improving conversion rates often involves optimising the landing page, ensuring it’s mobile-friendly, and aligning the SMS message with the page content.
Tracking these metrics over time helps identify patterns and optimise future campaigns for better engagement and revenue generation.
6. Monitoring Opt-Out Rates to Maintain a Healthy List
The opt-out rate is a vital metric for understanding customer satisfaction with your SMS campaigns. If your opt-out rate is higher than expected, it may indicate that:
- Message Frequency: You may be sending messages too often, leading to “message fatigue” and prompting customers to unsubscribe.
- Irrelevant Content: If recipients find the content irrelevant or uninteresting, they’re more likely to opt out.
By monitoring opt-out rates, you can adjust your messaging frequency, refine your audience segmentation, or improve personalisation to keep subscribers engaged.
7. Tools and Software for SMS Analytics
Many SMS providers offer built-in analytics tools, but businesses may also benefit from integrating with third-party analytics platforms for a deeper analysis. Here are some popular tools:
- Google Analytics: For campaigns that include links, Google Analytics can track website traffic, conversions, and user behaviour, allowing you to understand how SMS campaigns impact your online presence.
- CRM Integration: Integrating SMS with your CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software can provide a fuller view of customer interactions, showing how SMS fits into the broader customer journey and lifecycle.
- Built-In SMS Platform Analytics: Most SMS platforms offer dashboards with real-time metrics, including delivery rates, CTR, and opt-out rates. Look for a provider that offers detailed reporting to help you assess performance quickly and accurately.
8. Using Analytics for Continuous Improvement
The power of SMS analytics lies in the ability to make data-driven improvements. By analysing campaign performance over time, you can:
- Identify Trends: Recognise seasonal or behavioural trends that affect engagement, allowing you to align future campaigns with periods of high engagement.
- Refine Audience Segmentation: Use data to better understand your audience, refine segments, and deliver more targeted messages.
- Optimise Timing: Fine-tune the timing of your messages based on engagement trends, ensuring you reach customers when they’re most receptive.
Continual analysis helps ensure your SMS strategy remains effective, responsive to customer preferences, and aligned with your business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Bulk SMS
1. What is bulk SMS, and how does it work?
Bulk SMS is the practice of sending a large volume of SMS messages to multiple recipients simultaneously, typically for marketing or informational purposes. Bulk SMS services allow businesses to send messages through a specialised SMS platform or API that connects to mobile networks. Messages are transmitted from the business, routed through an SMS gateway, and then delivered to recipients' phones via mobile carriers. This technology makes it possible to reach a wide audience instantly, making it highly effective for time-sensitive communications, promotions, and customer engagement.
2. Why is bulk SMS effective compared to other marketing channels?
Bulk SMS is uniquely effective due to its high open rates, immediacy, and direct delivery to recipients’ mobile phones. Unlike email, which can get lost in spam or cluttered inboxes, SMS messages are read almost instantly, with over 90% of recipients opening messages within minutes of receipt. The personal nature of SMS also fosters a strong connection, as messages appear alongside personal contacts on users’ phones. For businesses, this means bulk SMS offers an unparalleled opportunity to reach customers quickly and effectively, especially for urgent updates, reminders, or promotions.
3. What industries benefit the most from bulk SMS?
Many industries can benefit from bulk SMS, especially those that rely on timely communication with customers. Key sectors that see value from SMS include:
- Retail: For promotions, sales alerts, and in-store events.
- Healthcare: For appointment reminders, health updates, and patient communication.
- Finance: For transaction alerts, payment reminders, and security notifications.
- Hospitality: For booking confirmations, reservation updates, and special offers.
- Education: For event notifications, closures, and timetable changes.
- Real Estate: For open house alerts, new listings, and follow-up communication.
Each of these industries leverages SMS to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and ensure effective communication.
4. How does the opt-in process work for SMS marketing?
The opt-in process is how businesses obtain permission from customers to send them SMS messages. According to Australian regulations, businesses must have consent before sending marketing SMS. Here’s how the opt-in process typically works:
- Explicit Opt-In: Customers actively choose to receive SMS messages by signing up through a website form, app registration, or in-store interaction.
- Double Opt-In: Some businesses use double opt-in, where customers confirm their subscription by replying to an initial SMS or clicking a link. This adds an extra layer of verification and ensures compliance.
- Clear Disclosure: The opt-in form should disclose what types of messages customers can expect and how often they’ll receive them. This transparency builds trust and sets clear expectations.
Businesses should document opt-in consent and ensure that they provide a straightforward opt-out option in every message to comply with the Spam Act 2003.
5. How do I calculate the cost of bulk SMS?
The cost of bulk SMS typically depends on the following factors:
- Number of Messages: SMS providers often charge on a per-message basis, though discounts may apply for higher volumes.
- Destination: Messages sent internationally may incur higher fees than domestic messages.
- Delivery Route: Some providers offer premium delivery routes for faster delivery, which can cost slightly more.
- Add-On Features: Features like customised sender IDs, delivery receipts, or integration with APIs may also affect pricing.
To calculate the cost, multiply the number of messages by the per-message fee. Many providers offer online calculators or pricing guides to help businesses estimate costs based on their specific needs.
6. Can I send SMS messages internationally?
Yes, many SMS providers offer international messaging, allowing businesses to reach global audiences. International SMS may have different rates depending on the destination country, as well as potential restrictions on message content, frequency, and opt-out requirements based on local regulations. It’s important to check with your SMS provider to understand these international considerations and ensure compliance with relevant laws.
7. What types of content are best suited for SMS messages?
Due to its character limits and direct nature, SMS is best suited for concise, actionable messages. Effective SMS content includes:
- Promotions and Discounts: Clear, time-sensitive offers that drive immediate action.
- Reminders: Appointment reminders, booking confirmations, and payment due dates.
- Alerts: Transaction alerts, delivery notifications, and security updates.
- Event Invitations: Notifications about upcoming events, launches, or sales.
- Two-Way Engagement: Interactive messages that invite responses, such as customer feedback, confirmations, or RSVPs.
Since SMS is a personal channel, keeping messages brief, relevant, and valuable to the recipient is essential for engagement.
8. How can I personalise SMS messages?
Personalising SMS messages helps increase engagement and make customers feel valued. Common methods include:
- Dynamic Fields: Many SMS platforms support dynamic fields that automatically insert customer-specific information (like first names, locations, or recent purchases) into messages.
- Segmentation: Group customers based on demographics, behaviour, or preferences, and send targeted messages to each segment.
- Customised Offers: Tailor promotions to individual customer history or preferences. For example, send a discount on a product category the customer has previously purchased.
Personalisation strengthens the impact of SMS campaigns by ensuring the message is relevant to each recipient.
9. Is it possible to include links or multimedia in SMS messages?
Yes, SMS messages can include links, and some SMS providers support Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) for sending images, audio, or video content. However, MMS messages can be more costly than standard SMS and may not be supported by all carriers. Including a link to a mobile-friendly landing page can be a great alternative, allowing businesses to convey more information and drive traffic to their website or online store.
10. How do delivery reports work for SMS messages?
Delivery reports (DLRs) provide data on whether an SMS message was successfully delivered to the recipient’s phone. Statuses may include:
- Delivered: The message reached the recipient’s phone.
- Failed: The message couldn’t be delivered, possibly due to an invalid number, network issues, or device problems.
- Buffered: The message is queued and will be delivered when the network is available.
Delivery reports are essential for tracking campaign success and identifying any issues with message delivery.
11. What should I do if my messages have a high opt-out rate?
If your messages have a high opt-out rate, it’s important to review your SMS strategy to understand the cause. Possible reasons for high opt-outs include:
- Message Frequency: Sending messages too frequently can lead to fatigue.
- Irrelevant Content: If the content doesn’t align with customer interests, they may unsubscribe.
- Timing: Messages sent at inconvenient times may frustrate recipients.
To address high opt-out rates, consider adjusting your messaging frequency, improving personalisation, or sending messages at more appropriate times.
12. Are there restrictions on the time I can send SMS messages in Australia?
Yes, the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) recommends that businesses avoid sending commercial SMS messages during “unsociable hours.” While there is no strict legal requirement, best practice is to send messages between 9 a.m. and 8 p.m. to avoid inconveniencing recipients. Avoid sending messages too early or late, as this can result in higher opt-out rates and customer complaints.
13. How can I ensure my SMS campaigns comply with Australian regulations?
To ensure compliance with Australian regulations, follow these guidelines:
- Obtain Consent: Make sure customers have opted in to receive SMS messages.
- Provide an Opt-Out Option: Every message should include instructions on how to unsubscribe, typically by replying “STOP.”
- Identify the Sender: Clearly identify your business in each message.
- Respect Privacy: Adhere to the Privacy Act 1988 by protecting customer data and using it only for the intended purpose.
By following these best practices, businesses can stay compliant and avoid fines or penalties from ACMA.
14. Can I schedule SMS messages in advance?
Yes, most SMS platforms allow businesses to schedule messages for specific dates and times. Scheduling is particularly useful for planned campaigns, such as seasonal promotions or reminder messages. By pre-scheduling, businesses can automate their SMS outreach, ensuring messages go out at optimal times without manual intervention.
15. What are the best practices for writing SMS messages?
For effective SMS messages, keep these best practices in mind:
- Be Clear and Direct: Communicate your message quickly, as you’re working within a character limit.
- Use a Strong CTA: Encourage action by including a clear call-to-action (e.g., “Shop Now,” “Reply YES”).
- Limit Abbreviations: While space is limited, avoid excessive abbreviations, which can make messages harder to read.
- Stay Professional: Use a friendly, professional tone that aligns with your brand voice.
Effective SMS messages are clear, actionable, and respectful of the customer’s time.
16. How does two-way SMS work, and what are its benefits?
Two-way SMS enables customers to respond directly to messages, making it possible for businesses to have interactive conversations. This functionality is valuable for:
- Customer Support: Customers can ask questions or request information directly via SMS.
- Confirmations: Customers can confirm appointments or reservations by replying to messages.
- Feedback: Businesses can collect feedback through short surveys or ratings.
Two-way SMS improves customer experience by making interactions convenient and accessible.
17. What’s the difference between SMS and MMS?
SMS (Short Message Service) and MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) are both messaging formats, but they differ in functionality:
- SMS: Limited to 160 characters and text-only.
- MMS: Supports multimedia content, such as images, videos, and audio, along with longer text messages.
While SMS is more widely supported and cost-effective, MMS can be useful for campaigns requiring rich media, like product images or promotional videos.
18. What are common challenges with bulk SMS, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges with bulk SMS include high opt-out rates, message delivery issues, and maintaining engagement. These can be addressed by:
- Regular List Maintenance: Remove inactive or incorrect numbers to improve delivery rates.
- Audience Segmentation: Send targeted messages that resonate with specific audience segments.
- Frequency Management: Avoid message fatigue by limiting the frequency of campaigns.
Regularly reviewing campaign performance and testing different strategies helps ensure your SMS campaigns remain effective.
19. Can I track conversions from SMS campaigns?
Yes, tracking conversions from SMS campaigns is possible by including unique links, promo codes, or call-tracking numbers in your messages. Link tracking can reveal how many recipients visited your site or completed a desired action. Integration with analytics tools or CRMs further enhances conversion tracking, providing insight into how SMS drives sales or other outcomes.
20. Is bulk SMS environmentally friendly?
Compared to direct mail or other traditional marketing methods, bulk SMS is more environmentally friendly, as it does not rely on physical materials like paper or ink. SMS’s digital nature minimises waste and carbon footprint, aligning with sustainability goals for businesses that prioritise eco-friendly practices.




